Ensuring High Component Quality with Recycled Plastics
As industries face pressure to adopt sustainable practices, post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics have become essential for reducing waste. However, the variability of PCR plastics presents challenges in maintaining product quality. Advanced technologies like dielectric sensors and AI-driven analytics provide real-time insights into material behavior, allowing manufacturers to visualize deviations and ensure that quality standards are met. The AVIDENS consortium combines expertise in materials science, sensor technology, and process parameters to support manufacturers. These tools enable the integration of PCR plastics into production while maintaining high-performance outcomes.
The Pressure to Adapt with Recycled Plastics and the Attractiveness of Germany as a Business Location
Around the world, industries are increasingly pressured to adopt environmentally responsible practices that align with international regulations. This shift is especially pronounced in the plastics sector, where global production exceeded 400.3 million metric tons in 2022 [1], driving the urgent need to reduce reliance on virgin materials and cut waste. At the center of these efforts is the push for post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics, a critical component of the circular economy.
However, the path from ambition to reality is filled with challenges. Regulations such as the EU Green Deal and the End-of-Life Vehicle Directive have set ambitious targets, particularly in the automotive industry. By 2030, these regulations require that 25% of all plastic used in vehicles come from PCR materials [2]. While this is a crucial step toward sustainable production, it introduces significant hurdles. Chief among them is ensuring that recycled materials, with all their inherent variability, meet the stringent performance standards required for modern components.
In contrast to European regulations and the challenges they bring, a survey by PlasticsEurope [3] reveals a concerning trend: Germany is becoming increasingly less attractive as a business location for plastics processors. This is clearly reflected in Stihl’s decision to relocate to neighboring Switzerland, which is far from being considered a low-wage country. The underlying issues, however, go much deeper.
The Complex Nature of Recycled Plastics
Unlike virgin plastics, which are produced under controlled conditions to ensure consistency, PCR plastics come with a diverse and often unpredictable history. These materials are sourced from a wide range of post-consumer products—from packaging to electronic waste—and their composition reflects this variability. Even after sorting and processing, PCR plastics can contain residual contaminants or mixed polymers, leading to significant challenges in manufacturing. This translates to the fact that most of the available PCR material is of lower quality in terms of purity – not to mention the traceability of the stream of material.
Adding to this complexity is the estimated 7.5-million-ton shortfall in high-quality PCR plastics [3].This shortage forces manufacturers to work with less consistent materials, introducing variability in material flow, crystallization rates, and final product stability. For molders, this variability can cause deviations that affect dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and issues in further process steps like coating.
At the same time, market demands remain as stringent as ever. Automotive manufacturers, for example, require parts that are durable, precise, and meet strict tolerances for fit and finish. Any inconsistencies in the molding process due to material variation can result in defective parts, increased waste, and costly rework. The challenge is clear: how can manufacturers incorporate recycled materials without sacrificing quality?
Addressing Material Deviations in the Molding Process
The inherent variability of PCR plastics presents risks at every stage of the molding process. Flow behavior, crystallization rates, and dimensional stability can all be affected by changes in material composition. For example, a batch of PCR material with higher levels of contaminants may cause uneven mold filling, which in turn affects cooling and leads to surface defects or weak structural points.
Crystallization rates are another critical factor. Different polymers can crystallize at varying speeds, leading to parts that are either too brittle or too flexible, depending on the composition. These deviations compromise both the strength and the dimensional accuracy of the product, often necessitating rework or scrapping of parts.
To manage these challenges, manufacturers need tools that offer real-time insights into material behavior during the molding process. This is where advanced sensor technology, particularly dielectric sensors, plays a crucial role.
How Dielectric Sensors Offer Critical Insights
Dielectric sensors are essential for monitoring material behavior in real time.
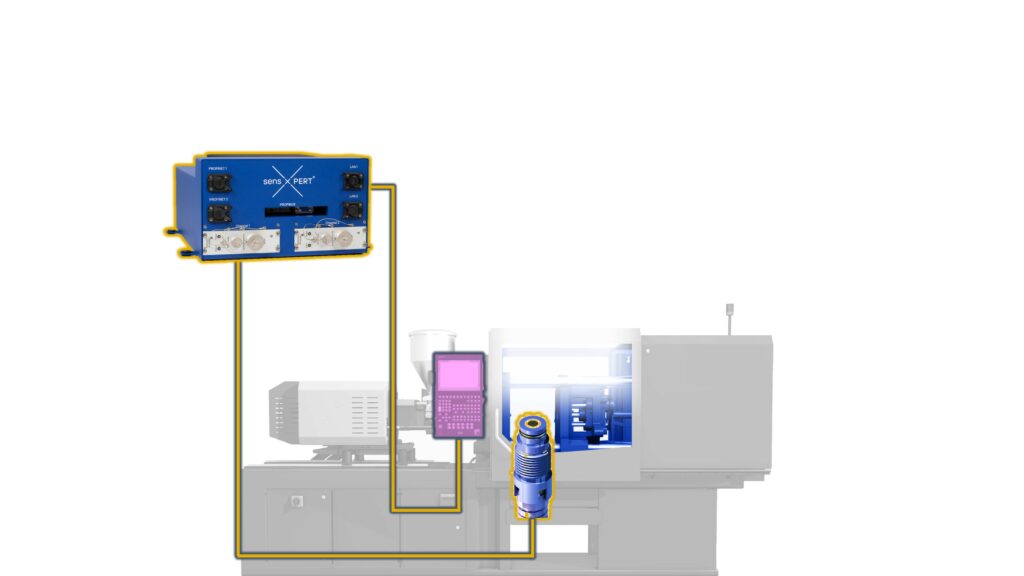
Unlike traditional temperature and pressure sensors, which provide only indirect data, dielectric sensors measure the electrical properties of the material itself, including the dielectric constant and loss factors. These properties shift in response to changes in material composition, flow behavior, and crystallization.
Placed directly within the mold, dielectric sensors track how the material flows and solidifies, offering manufacturers immediate feedback on its behavior. For example, shifts in the dielectric constant can indicate changes in viscosity, signaling potential flow issues or uneven filling of the mold. Similarly, fluctuations in loss factors can highlight differences in crystallization, allowing molders to detect structural defects early in the process.
This real-time data allows manufacturers to visualize material behavior and understand how deviations might affect the final product. By providing detailed, on-the-spot insights, dielectric sensors help ensure that PCR materials meet stringent quality standards despite their variability.
Visualizing Material Behavior for Real-Time Quality Control
The data gathered by dielectric sensors is transformed into visual representations, allowing manufacturers to compare material performance against predefined quality benchmarks. These real-time visualization tools are essential for molders working with PCR plastics, where deviations are common due to the inherent variability in the material.
Through real-time graphs and charts, manufacturers can monitor how the material flows, crystallizes, and solidifies. By comparing this visualized data with expected behavior, manufacturers can quickly determine if the material is meeting critical criteria such as dimensional stability, strength, and surface finish. For instance, a visualization might show that the crystallization rate is slower than anticipated, indicating potential issues with solidification or surface defects. These insights enable manufacturers to assess whether the material meets required standards, even when working with inconsistent PCR inputs. This transparency not only improves quality control but also builds confidence in the production process by providing data-driven insights.
Enhancing Visualization Insights with AI and Data Science
While dielectric sensors provide real-time data, AI and data science further enhance these insights by identifying patterns and potential deviations. AI models, trained on historical production data, analyze sensor inputs to detect subtle deviations that may not be immediately visible.
In this context, AI enhances the visualization tools by providing deeper insights into material behavior. By layering AI analysis on top of real-time sensor data, manufacturers can better understand how PCR materials behave under specific conditions and how these behaviors relate to product quality.
AVIDENS: A Consortium of Experts in Recycled Plastics Processing
AVIDENS is a consortium of experts dedicated to addressing the challenges of working with recycled plastics.

The consortium brings together sensXPERT (specialists in materials science, sensor technology, and AI), Schwarz Plastics Solutions (experts in plastics engineering), NETZSCH Analyzing & Testing (material analysis experts), and Precupa (precision mold makers). This collaboration combines expertise across the plastics value chain to provide comprehensive solutions.
In addition to these core partners, AVIDENS collaborates with Meraxis, a material distributor, and LabV, a provider of digital laboratory solutions. Together, they offer turnkey solutions for customers and hands-on support for their own production setups, addressing challenges from material qualification to process control.
A Sustainable Future with Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
The increasing reliance on PCR plastics presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. While recycled materials are crucial for achieving sustainability goals, their variability can introduce significant risks during production. By leveraging advanced technologies like dielectric sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time visualization tools, manufacturers can effectively manage these challenges.
These technologies ensure that recycled materials meet performance standards, reduce waste, and improve cycle times. Consortia like AVIDENS, which combine cutting-edge technology with deep industry expertise, provide invaluable support to manufacturers as they navigate the complexities of working with PCR plastics.
As the industry evolves, advanced manufacturing solutions will be key to balancing sustainability with quality—ensuring manufacturers meet both regulatory demands and market expectations.
Ensuring Consistent Quality in PCR Plastics
In our insightful webinar titled,“More Sustainability, Consistent Quality: How to successfully process PCR plastic” our experts will tackle one of the industry’s pressing challenges: ensuring consistent quality with post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics.
As more companies embrace sustainability, the use of PCR plastics is critical to reducing waste and achieving environmental targets, yet these materials often present quality consistency issues. This session will reveal cutting-edge solutions, such as dielectric sensors and AI-powered analytics, to provide real-time insights into material behavior.
Discover how to manage deviations dynamically, ensuring quality assurance and unlocking the potential of PCR integration into production. Register now to gain essential strategies and connect with industry leaders!

Sources:
[1] https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/
[2] https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/end-life-vehicles_en
[3] Kirr, K & Stahl, O.: ‘Kreislaufwirtschaft in der Kunststoffindustrie – Organisatorische Herausforderungen und Chancen’ Presentation from TecPart Annual Conference 2024