Next-Level Composites Manufacturing: A CosiMo Case

Next-Level Composites Manufacturing: A CosiMo Case
With an ever-increasing demand to implement sustainable practices in one’s daily life, such as opting for electric versus gas vehicles, there is also a growing demand for composites manufacturing. In the case of electric vehicles, for example, the car’s total weight influences its driving range. Therefore, engineers are compelled to use lightweighting materials, like composites, to ensure extended range and enhanced performance.
Composites are the preferred material in numerous industries, as they have several advantages and can be implemented in a wide range of applications. For electric vehicles, composite durability, chemical and corrosion resistance, and high performance under elevated temperatures are all especially valuable material characteristics.
In this article, we consider composites, their properties, and applications. Additionally, we highlight a research project during which sensXPERT contributed our Insight solution to optimize the high-volume production of carbon-fiber reinforced polymers. Finally, we touch upon the merits of digital composite manufacturing for energy saving, scrap rate reduction, and process efficiency.
Composites: Material Considerations
The combination of two or more materials with varying properties produces new composite materials. Each material comprising a composite has distinct properties that, when combined, form an enhanced material that exhibits evolved properties.
For this reason, composites have been wielded throughout numerous industries from aerospace and defense to sporting goods manufacturing.
The tailorability of composite materials allows for the development of composites with the following properties:
- High strength and durability,
- Design flexibility,
- Lightweight,
- High stiffness,
- Thermal conductivity,
- Chemical resistance,
- Among others.
Additionally, there are a number of popular polymer composite forms that are, according to their type, manufactured for specific applications; glass fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, and natural fiber-reinforced polymers to name a few.
The following case outlines a research project investigating the manufacturing of thermoplastic composite components using recycled glass-fiber non-woven materials.

CosiMo: Leveraging Machine Learning for Efficient High-Volume Composites Manufacturing
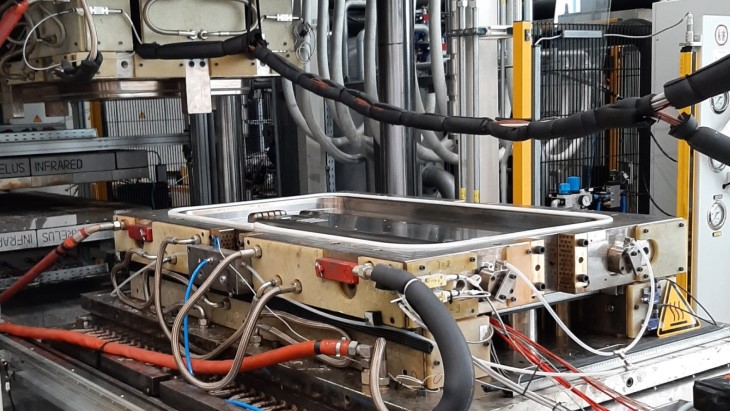
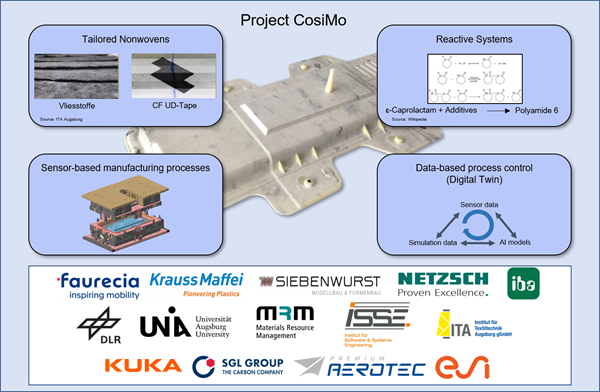
A three-year research project funded by the Bavarian government, CosiMo began in June 2018. This project brought together the University of Augsburg (MRM & ISSE), the German Aerospace Center, ITA Augsburg, and industrial partners including KUKA, Faurecia, Premium Aerotec, Krauss-Maffei, SGL-Carbon, NETZSCH, Siebenwurst, and IBA.

The CosiMo project was concerned with the manufacturing of components in their final shape using a single process step. More specifically, the project used compression-RTM technology for the in-situ polymerization of ɛ-Caprolactam, resulting in a polyamide 6 structure.
Accordingly, this process enables the sustainable, yet cost-effective production of lightweight components for the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
| The Key Concerns of the CosiMo Project |
|---|
| The impregnation of recycled glass-fiber non-woven materials through in-situ polymerization |
| The integration of reinforcement structures alongside load paths and metal inserts |
| The application of sensor-based process monitoring systems to collect process data |
| The development of virtual machine and process models using machine learning methods |
More information on the project is available on the University of Augsburg and the German Aerospace Center’s (DLR) websites.
sensXPERT’s Contribution to the CosiMo Project
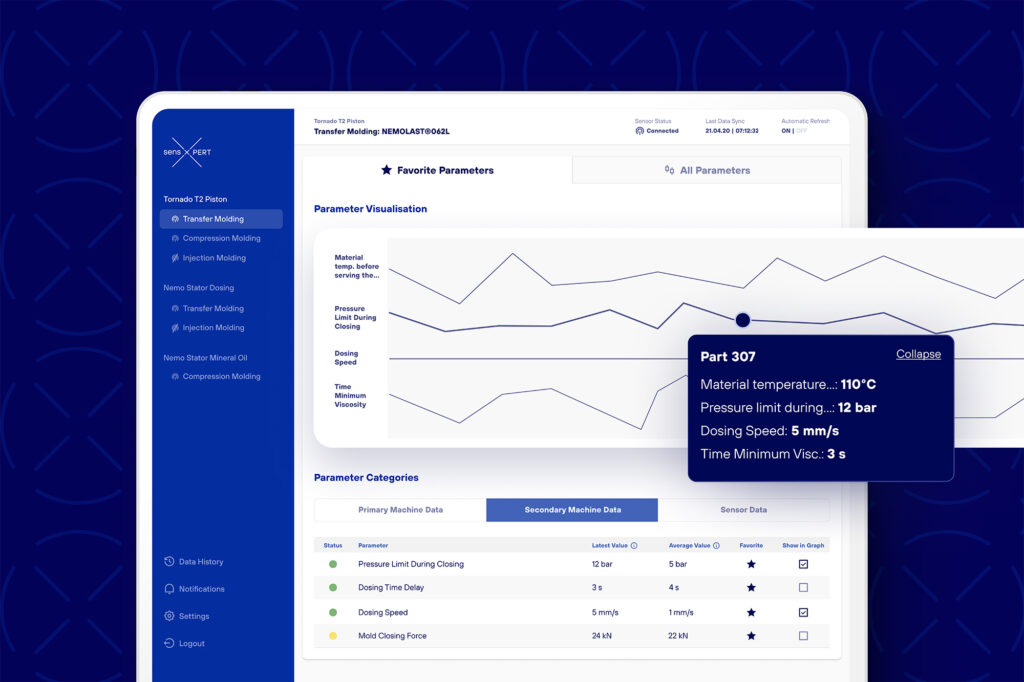
To contribute to the CosiMo project, sensXPERT provided our sensor-based monitoring system – sensXPERT Insight – to collect process data and develop machine learning models, as described above.
With the production of parts of complex geometries, the sensor network – which was developed in collaboration with project partners – monitored all process steps to ensure the necessary quality of the manufactured components in real-time.
sensXPERT’s durable sensors where integrated into the mold to measure crucial material properties, thus detecting the flow front and polymerization of the resin.
All of the collected sensor data was used to analyze the material’s polymerization behavior and optimize predictive models, which will be detailed below. Correspondingly, in-mold part quality was monitored in real-time, which eliminated the need for downstream quality assurance testing and generated significant time and resource savings.
Leveraging the power of machine learning
As mentioned, the collected real-time data is processed using machine learning techniques. Based on material science, the machine learning model continuously predicts the polymerization of the material during processing. Therefore, quality defects can be anticipated, and the production process can be adaptively controlled to prevent scrap or parts of low quality.
If you want to learn more about sensXPERT’s use of machine learning to create accurate predictive models, you can read our article ‘Presenting: The sensXPERT Way of AI’.
Transparent, Sustainable, Efficient Digital Composites Manufacturing
In the CosiMo project, sensXPERT’s contribution significantly supported the manufacturing of high-quality composite components. sensXPERT Insight allows for a highly productive and efficient production process, which translates into valuable time and resource savings. At the same time, the reduction of scrap rates and energy consumption is a considerable step towards more sustainable plastics production.
Overall, using digital solutions, such as sensXPERT Insight, to optimize processes for more transparent, sustainable, and efficient composites manufacturing is an increasingly important step to take towards becoming more resource efficient, compliant with new environmental regulations, aligned with consumer demands, and future-proof.
Sources
Center for Lightweight-Production-Technology – CosiMo – Composites for sustainable Mobility (dlr.de)