sensXPERT Material Characterization Sensors
Material characterization is invaluable in plastics manufacturing. Through the implementation of material characterization tests, manufacturers can ensure the quality, performance, and safety of their final products. There are numerous material characterization techniques and tests that can be conducted at different stages of production. This article will examine in-mold material characterization in specific. Additionally, we will shed light on the innovative sensXPERT material characterization sensors that monitor material properties during production to enhance control and quality in different manufacturing processes.
As a sensXPERT deep dive, over the next couple of weeks, we will also cover the other components of our Digital Mold solution; the Edge Device, WebApp, and Digital Cloud Service. If you want to discover the entire solution immediately, head to our ‘How does sensXPERT work?’ page and try the interactive AR Experience.
What is Material Characterization?
Material characterization methods are used to investigate and measure various materials to identify their physical, thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. Material characterization enables engineers to select the most suitable and appropriate materials for specific products, as well as ensure that final products are safe, efficient, and durable. Traditional material characterization techniques are conducted in laboratory settings, where environments are controlled, specialized personnel and equipment are readily available, and testing procedures are standardized.
However, conditions are not as regulated and controlled during plastics manufacturing as they are in a laboratory environment. Therefore, the material data gathered in a lab cannot be fully applied to material behavior and properties during production. Additionally, lab-based material characterization is not a real-time procedure, so it cannot account for fluctuating or dynamic circumstances within a manufacturing process.
So, what is the alternative? The answer is using industrial sensor technologies capable of conducting material characterization within the manufacturing environment, specifically to collect data on material behavior while it undergoes processing. To identify the properties of plastic materials in real-time, in-mold material characterization is necessary, which is why sensXPERT developed material characterization sensors to be directly integrated within the mold.
Sensor Technology
Before looking at sensXPERT’s material characterization sensors, it is worth highlighting the other types of sensor technologies that have been developed for applications in industries ranging from healthcare to consumer electronics. Sensor technologies aim to detect and measure physical properties or changes in the environment and convert them into electrical signals. The electrical signals are then processed, analyzed, and used for diverse applications.
Sensor technologies generally operate based on sensing principles, which relate to the physical properties the sensors are meant to determine. To name a couple of examples, the principle of thermal expansion or electrical resistance changes with temperature are two of the many methods that temperature sensors might wield.
What other types of sensor technologies are there?
We have touched upon material characterization sensors and will dive into them further. We also briefly mentioned temperature sensors, but beyond these two, several other sensor technologies are used in the plastics manufacturing industry. Among these are:
- Pressure sensors: to detect and measure pressure changes.
- Humidity sensors: which measure moisture content in the air.
- Proximity sensors: to detect the presence or absence of an object without physical contact.
- Flow sensors: to monitor the rate of flow in pipes and channels.
- Gas sensors: used to detect the presence and concentration of specific gases.
- Accelerometers: which measure acceleration forces and vibrations.
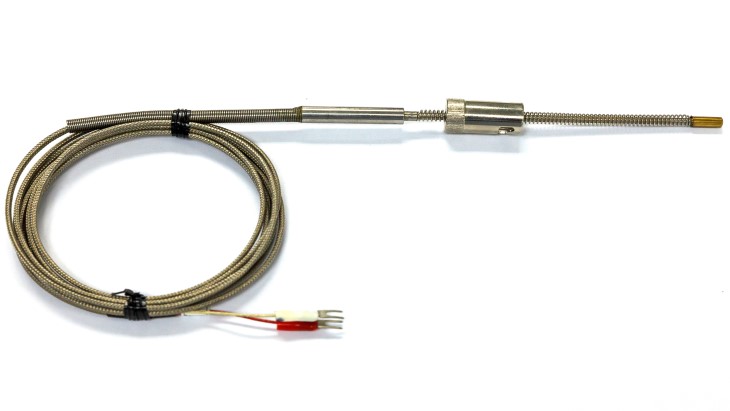
Pictured above: Thermocouple (Temperature Sensor)
How do in-mold material characterization sensors compare?
While the listed sensor technologies have their advantages, the specialized nature of in-mold material characterization sensors makes them distinctly valuable for plastics manufacturing. In-mold material characterization sensors are designed for specific use in plastics manufacturing processes, and their primary purpose is to provide real-time data on material behavior while it is being processed. The collection of real-time data also sets these sensors apart from the previously listed technologies, as instantaneous data enables manufacturers to monitor and adjust their process parameters directly. The other sensors may not be as immediately actionable during production. Additionally, in-mold material characterization sensors, as the name suggests, are integrated into the mold, which ensures their direct contact with the processed material.
Overall, the design, integration, and real-time data acquisition of in-mold material characterization sensors make them uniquely suited for optimizing manufacturing processes and guaranteeing final part quality and performance.
Deep Dive: sensXPERT Material Characterization Sensors
As part of the sensXPERT Digital Mold solution, sensXPERT’s material characterization sensors can monitor a variety of materials, including:
- Thermosets
- Thermoplastics
- Elastomers
- Composites
You can read more on the plastic industry’s materials landscape in this article.
The sensXPERT sensors uniquely make use of dielectric analysis (DEA), which examines how molecules behave in an electrical field. This data is then used to determine the material’s degree of cure or crystallization, viscosity, glass transition temperature, and more.
The sensors are placed in small holes in the mold to have direct, continuous contact with the material throughout its molding process. With this contact, the sensors can record changes in the material’s dielectric response.
sensXPERT’s material characterization sensors have been specially designed to withstand industrial manufacturing temperatures and pressures. The sensors are also scratch and solvent resistant. The highly durable sensors can steadily operate under temperatures of up to 280°C and pressures of up to 400 bar.
Moreover, all the data gathered by the sensors are transferred to the sensXPERT Edge Device, which will be expanded upon in next week’s blog post. This valuable real-time data is used to calculate and predict material properties that are critical to final part quality.
Stay on the lookout for next week’s article to learn more about the powerful sensXPERT Edge Device and how it uses machine learning algorithms to detect process patterns and deviations.